Learn how women can manage psoriasis symptoms and reduce flare-ups through effective treatments, lifestyle changes, and preventive care for healthier skin.
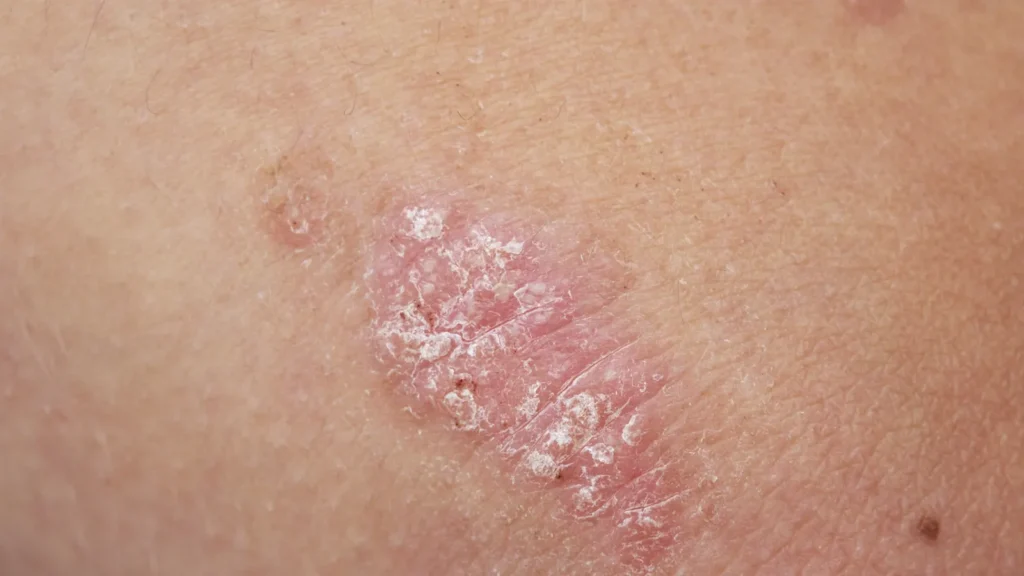
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of women worldwide, often leading to physical discomfort and emotional distress. Characterized by patches of thickened, scaly skin, the condition can appear anywhere on the body but most commonly affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. While psoriasis is not contagious, it significantly impacts quality of life, especially for women who may experience fluctuations in symptoms linked to hormonal changes, stress, and daily routines.
Understanding how psoriasis manifests and learning effective ways to manage flare-ups are key to living confidently with this condition. From identifying triggers to adopting the right treatments and self-care practices, women can take meaningful steps to minimize discomfort and protect their skin health long-term.
Understanding Psoriasis in Women and Its Causes
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system becomes overactive, speeding up the life cycle of skin cells. Instead of shedding naturally, new skin cells accumulate rapidly, forming thick, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales. The exact cause remains unclear, but a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors is believed to play a role.
1. Genetics:
Women with a family history of psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Research indicates that certain genes linked to immune function influence the body’s inflammatory response, making individuals more susceptible.
2. Hormonal Changes:
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone influence immune response and skin cell growth. Fluctuations during:
- Menstrual cycles
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
3. Stress:
Emotional or physical stress can weaken the immune system, leading to flare-ups.
4. Infections:
Infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, can trigger psoriasis episodes, especially in the case of guttate psoriasis.
5. Skin Trauma:
Injuries such as cuts, sunburns, or insect bites can induce psoriasis plaques through the Koebner phenomenon.
6. Medications:
Certain drugs may worsen psoriasis, including:
- Beta-blockers (used for hypertension)
- Lithium (used for bipolar disorder)
- Antimalarial drugs
7. Lifestyle Factors:
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase inflammation and severity.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is linked to increased risk and severity.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking can impair immune function and trigger flare-ups.
8. Immune System Imbalance
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This abnormal immune response leads to inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover, which creates visible plaques.
9. Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers
Stress, infections, cold weather, alcohol, and certain medications can trigger or worsen psoriasis. Skin injury from cuts, burns, or even tattoos can also lead to new patches in a phenomenon known as the Koebner effect.
Recognizing Symptoms of Psoriasis in Women
The signs and severity of psoriasis vary, but common symptoms include:
-
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery-white scales.
-
Itching, burning, or soreness around affected areas.
-
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed.
-
Thickened or ridged nails, often discolored or brittle.
-
Joint pain and stiffness, which can indicate psoriatic arthritis.
In women, psoriasis may appear more prominently on visible areas like the scalp, face, or hands, making it not just a medical issue but also a source of emotional stress. Many women report feelings of self-consciousness or anxiety during flare-ups, emphasizing the importance of emotional well-being in managing the condition.
How Psoriasis Affects Women
Women with psoriasis often face specific challenges, including:
- Hormonal Influences: Fluctuations during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause can alter disease severity.
- Pregnancy and Postpartum: Some women notice improvement during pregnancy, while others experience worsening symptoms postpartum.
- Psychosocial Impact: Visible skin lesions can impact self-esteem, body image, and mental health.
- Management Challenges: Hormonal changes may influence response to treatment.
Managing Psoriasis Symptoms and Flare-Ups
Effective psoriasis management involves a combination of medical treatment, skincare, and lifestyle changes. Since triggers and severity differ among individuals, women should work closely with dermatologists to develop a personalized plan.
1. Medical Treatments
Topical Therapies:
For mild to moderate psoriasis, creams and ointments containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or salicylic acid can reduce inflammation, scaling, and redness.
Phototherapy:
Light therapy involves exposing affected skin to controlled ultraviolet light, which helps slow down skin cell production. This treatment is particularly effective for widespread or resistant cases.
Systemic Medications:
For severe or persistent psoriasis, oral or injectable medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics (like adalimumab or secukinumab) can help regulate the immune response. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should discuss medication safety with their healthcare provider.
2. Skincare Routine and Self-Care
-
Moisturize frequently: Choose thick, fragrance-free moisturizers to prevent dryness and cracking.
-
Gentle cleansing: Use mild soaps or cleansers, and avoid long, hot showers that strip natural oils.
-
Avoid scratching: Itching worsens inflammation and can cause infections. Apply cool compresses or anti-itch lotions instead.
-
Protect your skin: Wear sunscreen daily to avoid sunburns, which can trigger new lesions.
3. Diet and Nutrition
An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber supports immune balance. Foods like salmon, walnuts, leafy greens, and berries may help reduce flare-ups. Limiting alcohol, red meat, and processed foods can also improve skin health.
4. Stress Management
Stress is one of the most powerful triggers of psoriasis flare-ups. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, journaling, or even short daily walks can help reduce anxiety. For busy women, dedicating 10–15 minutes a day to relaxation can make a significant difference.
5. Hormonal and Life Stage Considerations
-
During Pregnancy: Many women experience remission or improvement, but some may require specialized care for safe medication use.
-
Postpartum Period: Hormonal shifts can trigger flare-ups, so maintaining a consistent skincare and stress management routine is essential.
-
Menopause: Reduced estrogen can dry the skin, so richer moisturizers and medical treatments may be necessary.
Preventing Psoriasis Flare-Ups
While psoriasis cannot be cured, flare-ups can be significantly reduced through proactive prevention strategies.
-
Identify personal triggers: Keep a journal of foods, stress levels, weather changes, and skincare products to identify what worsens your condition.
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase inflammation and reduce treatment effectiveness.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol: Both are linked to increased psoriasis severity and slower healing.
-
Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake supports overall skin elasticity and health.
-
Seek regular care: Schedule dermatology visits every few months to monitor progress and adjust treatments.
FAQ: Psoriasis in Women
1. Can psoriasis go away permanently?
No, psoriasis is a chronic condition. However, with proper management and consistent treatment, women can experience long periods of remission without symptoms.
2. Can stress alone cause psoriasis?
Stress doesn’t cause psoriasis, but it can trigger or worsen flare-ups by increasing inflammation in the body.
3. Is psoriasis hereditary?
Yes, genetics play a role. Having a parent or sibling with psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
4. Are natural remedies effective for psoriasis?
Some natural remedies—such as aloe vera, oatmeal baths, and coconut oil—can soothe irritation and reduce scaling, but they should complement medical treatments.
5. Can psoriasis affect fertility or pregnancy?
Psoriasis does not directly affect fertility, but some medications used to treat it may not be safe during pregnancy. Women should consult their healthcare provider before planning pregnancy.
Conclusion
Psoriasis in women is a lifelong condition, but it doesn’t have to define one’s life. With the right combination of medical treatment, skincare, diet, and emotional care, flare-ups can be controlled and minimized. Awareness and proactive management are key—especially as hormonal changes, stress, and environmental triggers play a role in symptom intensity.
Empowerment begins with knowledge. By understanding their skin’s needs, women can build confidence, manage psoriasis effectively, and embrace every stage of life with resilience and care.



Pingback: Women’s Skin Health: Complete Guide to Common Skin Condition - SheCure