Learn about the causes, symptoms and signs, and effective treatments for eczema and dermatitis in women, plus prevention tips for long-term skin health.
Eczema and dermatitis are among the most common chronic skin conditions affecting women worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, dryness, and itching, these conditions can impact more than just physical comfort—they often influence self-esteem and daily confidence. Hormonal fluctuations, environmental factors, and stress all play significant roles in triggering flare-ups.
While anyone can develop eczema, women often face unique challenges due to hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Understanding these triggers and learning effective prevention strategies can help women regain control over their skin health and reduce discomfort.
Signs of Eczema and Dermatitis in Women
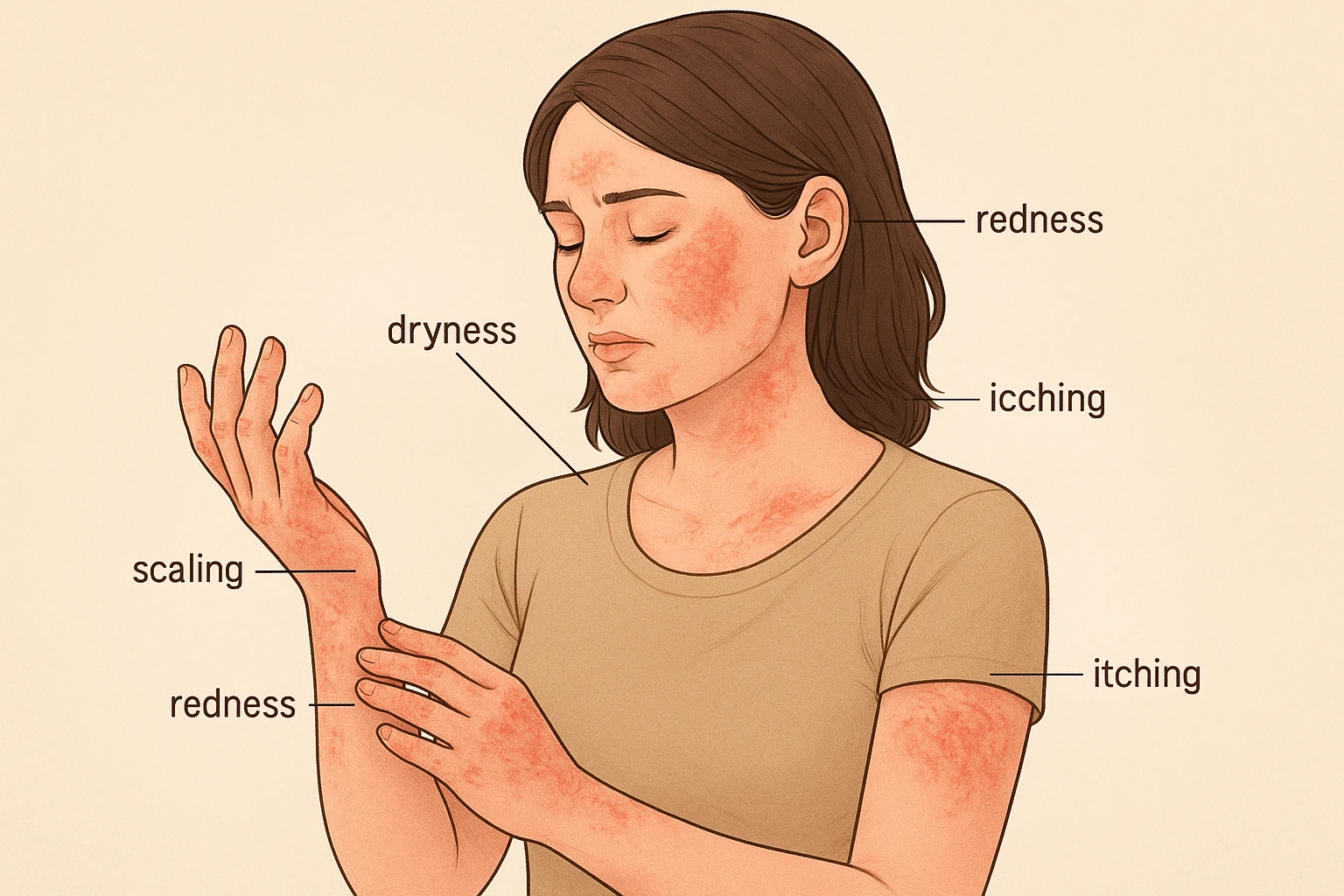
Recognizing the signs early can help in managing and seeking appropriate treatment. Here are some common signs of eczema and dermatitis in women:
- Redness and Inflammation: Areas of the skin may appear red, inflamed, or swollen, especially on the hands, face, neck, or creases of the elbows and knees.
- Itching: Intense itching is a hallmark symptom, often leading to scratching, which can worsen the skin condition.
- Dry, Scaly Skin: The skin may become dry, rough, and flaky, sometimes with visible scaling or peeling.
- Rash or Bumps: Raised bumps, blisters, or patches of rash may develop, sometimes oozing or crusting.
- Thickened or leathery Skin: Chronic scratching or rubbing can cause skin to thicken and become leathery (lichenification).
- Discoloration: Skin may appear darker or lighter in affected areas over time.
- Cracking and Bleeding: Severe dryness can lead to cracks in the skin, which may bleed or become infected.
- Areas of Skin Breakdown: In some cases, skin may become raw, sore, or inflamed due to persistent irritation.
Common Sites for Women:
- Hands and fingers
- Face, especially around the eyes or mouth
- Neck and chest
- Inner elbows and behind the knees
- Wrists
Common Triggers of Eczema and Dermatitis in Women
Eczema and dermatitis have complex causes that vary from person to person, but certain triggers are more prevalent among women due to biological and lifestyle factors.
1. Hormonal Changes
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone directly affect skin barrier function and oil production. Many women notice that their eczema symptoms worsen before menstruation, during pregnancy, or in menopause. Lower estrogen levels can cause dry skin, which weakens the skin’s ability to retain moisture and resist irritation.
2. Stress and Emotional Strain
Stress is one of the most powerful eczema triggers. Emotional strain leads to the release of cortisol, a stress hormone that disrupts immune balance and increases inflammation. For working women juggling careers and home responsibilities, chronic stress can worsen both the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups.
3. Environmental Factors
Dry air, extreme weather, and pollution often contribute to eczema symptoms. Urban environments with high exposure to dust and chemical irritants can weaken the skin barrier. Likewise, hot climates and air conditioning can strip moisture from the skin, leading to dryness and irritation.
4. Allergens and Irritants
Women frequently come into contact with cosmetic products, detergents, or fragrances that can trigger contact dermatitis. Common irritants include nickel in jewelry, harsh soaps, and certain skincare ingredients like alcohol or sulfates.
5. Dietary Sensitivities
Some women experience eczema flare-ups after consuming specific foods such as dairy, eggs, soy, or gluten. Although not all cases of eczema are allergy-related, identifying and avoiding trigger foods can significantly reduce inflammation and itching.
6. Genetic Predisposition
A family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever increases the likelihood of developing eczema. In such cases, maintaining consistent skincare routines and early preventive care are essential for long-term management.
Relief and Treatment Options
Finding relief from eczema and dermatitis involves a combination of medical care, skincare routines, and lifestyle modifications. Each woman’s treatment plan may vary depending on severity, triggers, and skin sensitivity.
1. Moisturizing and Barrier Repair
The cornerstone of eczema management is keeping the skin moisturized. Women should choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers containing ceramides, shea butter, or hyaluronic acid. Applying moisturizer immediately after bathing helps lock in hydration and repair the skin barrier.
2. Topical Medications
For moderate to severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors. These medications reduce inflammation and relieve itching but should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects from overuse.
3. Managing Stress and Emotional Health
Mind-body practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help lower cortisol levels and improve immune balance. Regular relaxation techniques are essential for women whose eczema is linked to stress or anxiety.
4. Gentle Skincare Routine
Avoid hot showers, harsh soaps, and exfoliating scrubs that can damage the skin’s protective layer. Instead, use mild, pH-balanced cleansers and pat the skin dry instead of rubbing. Choosing non-irritating fabrics like cotton also helps prevent friction-based irritation.
5. Phototherapy
Light therapy or phototherapy is sometimes recommended for chronic eczema cases that don’t respond to creams. Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light helps reduce inflammation and itching while promoting healthy skin regeneration.
6. Diet and Nutrition
An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and probiotics can improve skin health. Foods like salmon, flaxseeds, spinach, and yogurt may reduce inflammation and improve the skin barrier. Staying hydrated and reducing processed foods also supports skin healing.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Preventing eczema flare-ups requires consistent care and awareness of environmental and internal triggers.
1. Identify and Avoid Triggers
Keep a skin diary to record flare-up patterns, products used, foods eaten, and stress levels. Over time, this helps identify personal triggers and eliminate avoidable irritants.
2. Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine
Even when symptoms improve, women should continue moisturizing and protecting their skin daily. A consistent routine helps strengthen the skin barrier and prevent recurrence.
3. Protect Skin from Weather Changes
Use humidifiers in dry climates, wear gloves in winter, and apply sunscreen daily. UV protection not only prevents irritation but also reduces the risk of pigmentation after inflammation.
4. Regular Checkups with a Dermatologist
Persistent or worsening eczema should be examined by a professional. A dermatologist can identify underlying conditions like contact dermatitis, psoriasis, or allergies that may mimic eczema.
5. Mind-Body Balance
Maintaining mental and emotional health through rest, mindfulness, and supportive relationships is crucial. Women who manage stress effectively often experience fewer and less severe eczema episodes.
FAQ: Understanding Eczema and Dermatitis in Women
1. Can hormonal changes alone cause eczema in women?
Not directly, but they can worsen existing conditions by disrupting the skin barrier and increasing dryness or sensitivity.
2. Is eczema contagious?
No. Eczema and dermatitis are inflammatory, not infectious, and cannot spread through physical contact.
3. Are natural remedies effective for eczema?
Yes, to an extent. Aloe vera, coconut oil, and oatmeal baths can soothe inflammation. However, they should complement—not replace—medical treatments.
4. How can I prevent flare-ups during stressful periods?
Incorporate regular stress management techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and adequate sleep. Maintaining consistent skincare also helps reduce flare-ups.
5. Should I change my diet if I have eczema?
Not always, but identifying food sensitivities through elimination diets or allergy testing can help manage flare-ups in some women.
Conclusion
Eczema and dermatitis are not merely surface-level conditions—they reflect the body’s complex response to internal and external stressors. For women, hormonal shifts, emotional well-being, and environmental exposures all contribute to how the skin reacts and heals.
Managing these conditions requires a holistic approach: balanced nutrition, gentle skincare, consistent hydration, and emotional self-care. With awareness, prevention, and proper medical guidance, women can keep eczema under control and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.


Pingback: Women’s Skin Health: Complete Guide to Common Skin Condition - SheCure