Learn about common fungal infections in women, including candidiasis and skin fold rashes. Discover symptoms, causes, and prevention tips for lasting relief.
Fungal infections are a common but often uncomfortable reality for many women. They occur when fungi—organisms that thrive in warm, moist environments—overgrow on the skin, in body folds, or within the vaginal area. Among the most prevalent types affecting women are cutaneous (skin) fungal infections and candidiasis, commonly known as yeast infections.
While these conditions are rarely life-threatening, they can cause irritation, discomfort, and recurring symptoms that impact daily life. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting effective prevention habits can help women maintain healthy skin and overall hygiene.
Common Types of Fungal Infections in Women
1. Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
Candidiasis is caused by Candida albicans, a yeast that naturally lives in the body but can overgrow when the balance of microorganisms is disrupted. Vaginal yeast infections are particularly common, affecting up to 75% of women at least once in their lifetime.
Symptoms include:
-
Intense itching or burning sensation in the vaginal area
-
Thick, white, “cottage cheese-like” discharge
-
Redness, swelling, and irritation of the vulva
-
Pain during urination or sexual intercourse
Candidiasis can also affect other areas such as the mouth (oral thrush) or skin folds (cutaneous candidiasis).
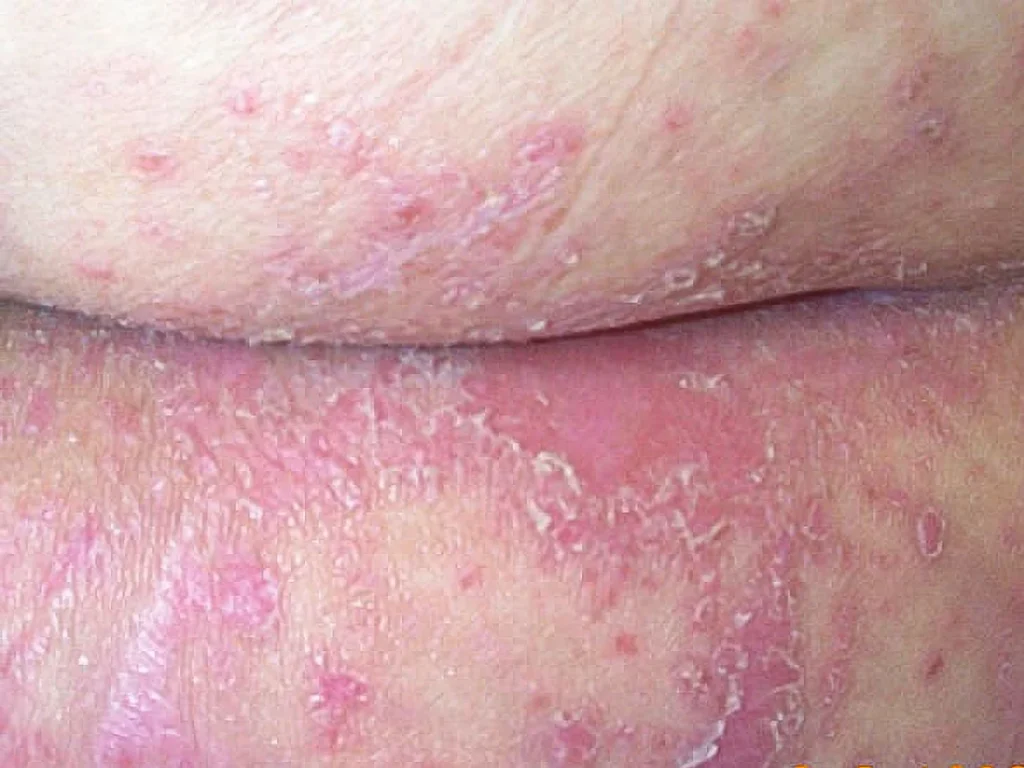
2. Intertrigo (Skin Fold Fungal Infection)
Intertrigo occurs when skin folds trap moisture, creating an ideal environment for fungal growth. It is common under the breasts, between thighs, under the belly, or around the groin.
Typical symptoms:
-
Red, shiny rash that may ooze or crack
-
Burning or itching sensation
-
Unpleasant odor due to secondary bacterial infection
This condition often worsens with heat, humidity, tight clothing, or obesity.
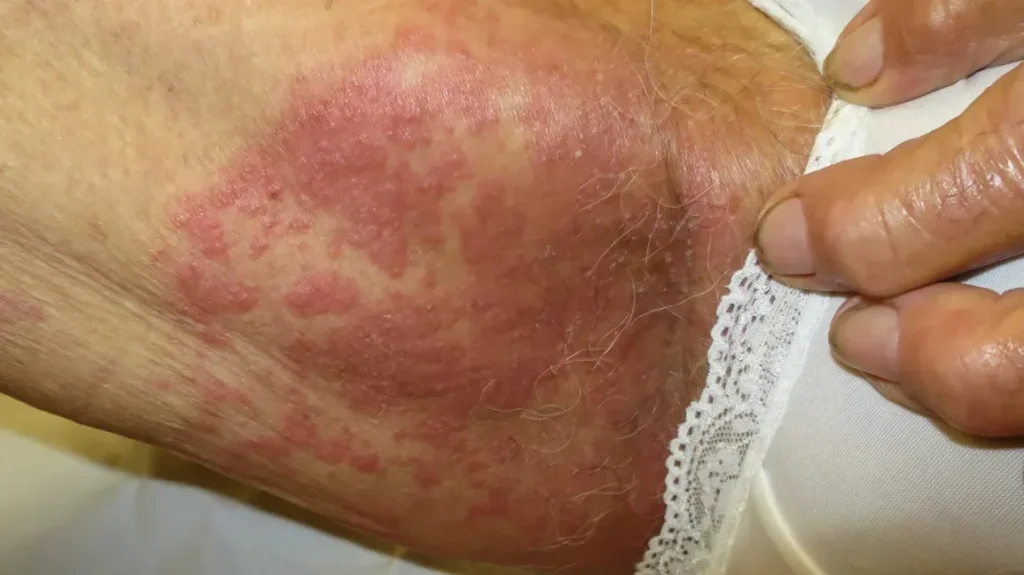
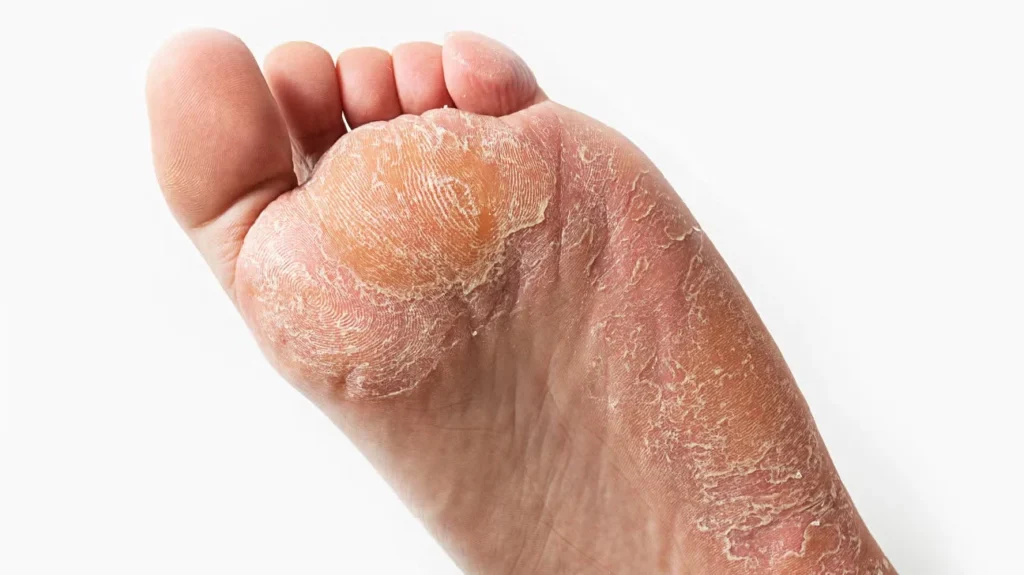
3. Tinea Infections (Ringworm and Athlete’s Foot)
Tinea infections are caused by dermatophyte fungi and can affect various body parts:
-
Tinea corporis: Ringworm on the body, forming circular red rashes.
-
Tinea pedis: Athlete’s foot, common between toes.
-
Tinea cruris: Jock itch, often seen in the groin area.
These infections spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, towels, or clothing and can be more frequent in women who exercise regularly or sweat excessively.
Causes and Risk Factors
Fungal infections in women can arise from multiple factors that disrupt the natural microbial balance or increase skin moisture retention.
Common causes include:
-
Excessive sweating and tight clothing that traps moisture
-
Poor hygiene or delayed changing of damp clothes
-
Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause
-
Use of antibiotics that destroy healthy bacteria
-
Weakened immune system due to stress, diabetes, or medication
-
Hot, humid climates that promote fungal growth
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as wearing synthetic fabrics, sharing personal items, or not drying skin properly after bathing increase infection risk.
Effective Treatments and Remedies
Treating fungal infections requires addressing both symptoms and underlying causes.
1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antifungal Treatments
Creams, ointments, and powders containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine are effective for most mild skin and vaginal infections.
2. Prescription Medications
For severe or recurrent infections, doctors may prescribe oral antifungals like fluconazole or itraconazole. Vaginal suppositories and medicated creams are also available for persistent yeast infections.
3. Natural and Home Remedies
While medical treatment is primary, some natural remedies can support healing:
-
Coconut oil: Contains antifungal properties that help soothe skin irritation.
-
Tea tree oil: Effective against yeast and dermatophyte fungi, but should be diluted before application.
-
Probiotics: Help restore healthy vaginal flora, reducing recurrence.
-
Apple cider vinegar baths: May balance skin pH and reduce fungal overgrowth.
4. Hygiene and Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Keep affected areas clean and dry.
-
Wear breathable cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing.
-
Change out of sweaty clothes immediately after exercise.
-
Use mild, fragrance-free soaps to avoid irritation.
Prevention Tips for Long-Term Protection
Preventing fungal infections requires consistent hygiene and awareness of personal habits.
Practical prevention tips:
-
Avoid prolonged moisture by patting skin dry after bathing.
-
Alternate shoes and let them air out daily.
-
Use antifungal powders if prone to sweating.
-
Maintain balanced blood sugar levels if diabetic.
-
Strengthen the immune system through proper nutrition, sleep, and stress management.
-
Avoid douching or using harsh feminine hygiene products that disrupt vaginal flora.
When to See a Doctor
While most fungal infections are manageable at home, medical attention is necessary when:
-
Symptoms persist after OTC treatment
-
The infection spreads or becomes painful
-
Recurrent vaginal infections occur more than four times a year
-
There are accompanying symptoms like fever, fatigue, or swelling
Doctors can perform laboratory tests to identify the specific fungus and prescribe targeted medication for effective relief.
FAQs About Fungal Infections in Women
1. Can hormonal changes increase fungal infection risk?
Yes. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can disrupt the body’s natural pH balance, promoting fungal overgrowth.
2. Is it safe to use antifungal creams during pregnancy?
Topical antifungal treatments are generally safe, but oral medications should only be taken under medical supervision.
3. How can I prevent fungal infections after workouts?
Change into dry clothes immediately, shower promptly, and apply antifungal powder to reduce moisture in skin folds.
4. Can diet affect fungal infections?
Yes. Diets high in sugar can promote fungal growth. Eating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and reducing processed sugar may help prevent recurrences.
Conclusion
Fungal infections in women—whether on the skin, in folds, or as vaginal candidiasis—can cause significant discomfort, but they are manageable and preventable with proper care. Understanding the triggers, maintaining good hygiene, and making small lifestyle changes can go a long way toward preventing future flare-ups. For persistent or recurrent infections, seeking medical advice ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
By taking a proactive approach, women can maintain healthy skin and intimate wellness, free from the irritation and discomfort of fungal infections.


Pingback: Candidiasis (Yeast Infection): Managing, and Preventing It in Women
Hello! I sent a request, but have not yet received a response.
What was the request?