Tracking hormonal changes throughout your menstrual cycle can help you understand your body better, identify patterns, and manage symptoms. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you track these changes effectively:
1. Understanding the Menstrual Cycle.
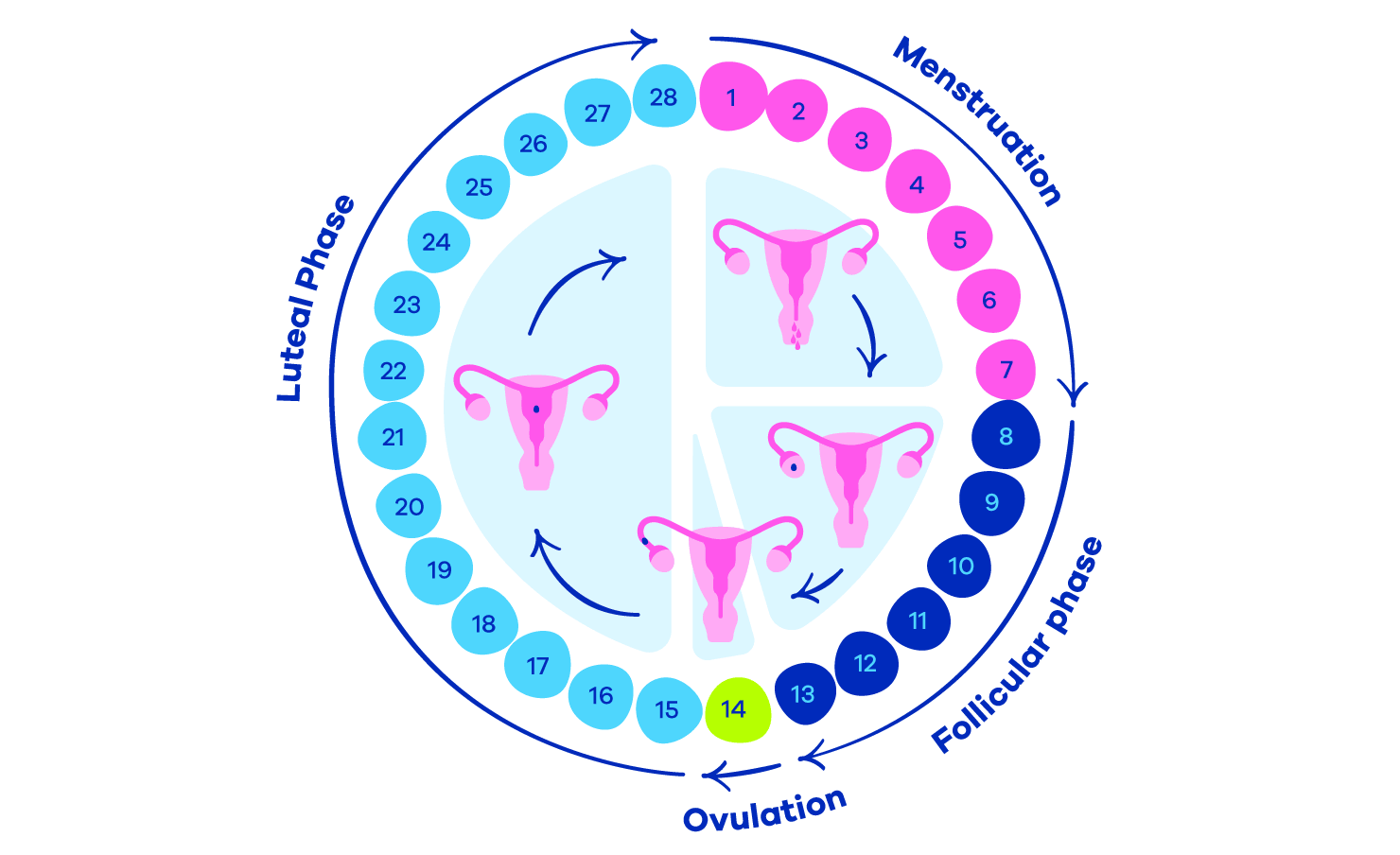
The menstrual cycle typically lasts 28 days but can range from 21–35 days. It is divided into four phases, each driven by hormonal fluctuations:
➤ Menstrual Phase (Days 1–5) – Period Starts
- What happens? The uterus sheds its lining, leading to menstruation (your period).
- Hormones:
- Estrogen & Progesterone: Low
- FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone): Starts rising to stimulate egg growth
- Symptoms: Cramps, fatigue, bloating, headaches, mood swings.
➤ Follicular Phase (Days 6–14) – Egg Matures
- What happens? The body prepares for ovulation; the uterine lining thickens.
- Hormones:
- Estrogen: Rises, boosting energy and mood
- FSH: Peaks to stimulate egg development
- Symptoms: Increased energy, glowing skin, better mood, high libido.
➤ Ovulatory Phase (Days 14–16) – Fertility Peak
- What happens? A mature egg is released from the ovary. This is the most fertile time in the cycle.
- Hormones:
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Surges to trigger ovulation
- Estrogen: At peak
- Progesterone: Begins rising
- Symptoms: Cervical mucus becomes clear & stretchy (like egg whites), body temperature rises, increased libido, mild cramps.
➤ Luteal Phase (Days 17–28) – Prepping for Next Cycle
- What happens? If the egg isn’t fertilized, hormone levels drop, signaling the next period.
- Hormones:
- Progesterone: Rises first, then falls if no pregnancy
- Estrogen: Drops
- Symptoms: PMS (bloating, mood swings, breast tenderness, fatigue, food cravings).
2. Hormonal Fluctuations and Their Effects
Each hormone affects the body differently throughout the cycle.
| Hormone | Main Function | Effects on Mood & Body |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogen | Prepares the body for ovulation | Boosts mood, skin health, energy, and libido |
| Progesterone | Prepares the body for pregnancy | Causes PMS, bloating, fatigue, and cravings |
| LH & FSH | Stimulate ovulation and egg growth | Can cause ovulation pain, mild cramps |
3. Methods to Track Hormonal Changes
➤ Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Tracking
- How it works: Take your temperature first thing in the morning before getting out of bed.
- What to look for:
- A slight dip before ovulation
- A rise of 0.5–1°F after ovulation due to progesterone increase
- Best for: Identifying ovulation and fertility windows.
➤ Cervical Mucus Monitoring
- How it works: Check vaginal discharge daily.
- What to look for:
- Dry or sticky (after period) – Low fertility
- Creamy or white (before ovulation) – Medium fertility
- Clear, stretchy, egg-white-like (ovulation) – High fertility
- Thicker or dry (luteal phase) – Low fertility
➤ Hormone Tracking Kits
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): Test for LH surge before ovulation.
- Progesterone Tests: Confirm ovulation by detecting progesterone levels.
➤Use a Tracking Tool
- Menstrual Cycle Apps: Use apps like Clue, Flo, or Kindara to log symptoms, moods, and cycle length.
- Paper Charting: Create a chart to record daily observations (e.g., basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and symptoms).
4. Signs & Symptoms to Watch For
➤ Mood & Mental Health Changes
- Follicular Phase: High energy, motivation, and confidence.
- Luteal Phase: Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression (PMS).
➤ Skin & Hair Changes
- Estrogen dominance (Follicular phase): Clear, glowing skin.
- Progesterone increase (Luteal phase): Increased oiliness and acne.
➤ Appetite & Metabolism Shifts
- Ovulation: Faster metabolism, reduced appetite.
- Luteal phase: More hunger, sugar cravings.
5. How Lifestyle Affects Hormonal Balance
➤ Diet & Nutrition for Hormone Regulation
- Healthy fats (avocados, nuts, salmon): Support hormone production.
- Protein & fiber (lean meats, beans, greens): Help stabilize blood sugar.
- Avoid excessive sugar & caffeine: Prevents hormone crashes.
➤ Exercise & Movement
- Follicular phase: High-intensity workouts (HIIT, cardio).
- Luteal phase: Gentle exercises (yoga, pilates, walking).
➤ Stress Management
- Why? High stress increases cortisol, which disrupts hormonal balance.
- Solutions: Meditation, deep breathing, journaling, quality sleep.
6. Using Tracking for Health & Fertility
➤ Understanding Your Fertile Window
- Ovulation usually happens around Day 14 (but varies).
- The 5 days before ovulation + ovulation day = highest chance of pregnancy.
➤ Identifying Hormonal Imbalances
- Irregular cycles (too short, too long, missing periods): Could indicate PCOS, thyroid issues, or stress.
- Extreme PMS: Could be a sign of estrogen dominance or progesterone deficiency.
➤ When to Seek Medical Advice
- Cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days.
- Severe PMS, unbearable cramps, heavy bleeding.
- No period for 3+ months (not due to pregnancy or menopause).
Why Track Hormonal Changes?
- Understand Your Cycle – Predict ovulation and menstruation.
- Manage Symptoms – Identify patterns in mood, skin, and energy levels.
- Optimize Fertility – Increase chances of conception or plan contraception naturally.
- Detect Hormonal Imbalances – Help diagnose conditions like PCOS, thyroid disorders, or menopause-related changes.
Also read about: 5 Natural Remedies for Managing Uterine Fibroids.
Resources:
- [Link to a related article “Fertility Awareness Methods “]
- [Link to “The Menstrual Cycle: Phases of Your Cycle”]
Conclusion:
Tracking hormonal changes throughout your menstrual cycle provides valuable insight into your body’s natural rhythms. By understanding how estrogen, progesterone, LH, and FSH fluctuate in each phase, you can predict ovulation, manage PMS symptoms, and optimize your overall well-being.
Using methods like basal body temperature tracking, cervical mucus monitoring, hormone test kits, and cycle-tracking apps, you can accurately map your cycle and detect any irregularities. Recognizing physical and emotional shifts—such as mood swings, energy fluctuations, skin changes, and appetite variations—helps you make informed lifestyle choices regarding nutrition, exercise, and stress management to support hormonal balance.
By consistently tracking your cycle, you can:
✅ Improve menstrual health and predict your period.
✅ Identify fertile windows for pregnancy planning or natural contraception.
✅ Recognize signs of hormonal imbalances (such as PCOS, thyroid issues, or irregular cycles).
✅ Know when to seek medical advice for persistent issues.
Ultimately, cycle tracking empowers you to take control of your reproductive health, enhance your quality of life, and make proactive decisions that support both physical and emotional well-being. Whether your goal is hormone balance, fertility awareness, or symptom management, understanding your cycle is a powerful tool for self-care.

Pingback: The Connection Between Thyroid Disorders and Weight Gain.
Pingback: PCOS vs Endometriosis: Key Differences & Overlaps
Pingback: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment for Acne Vulgaris in women